Japanese Group Sees Carbon Recycled Methane as Zero-emission Ship Fuel
Ship Carbon Recycling Working Group of Japan's Carbon Capture & Reuse Study Group has said that carbon recycled methane produced by methanation technology can be recognized as zero-emission ship fuel.
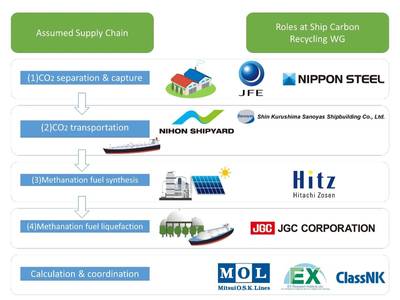
Methanation has been described as a technology for synthesizing methane, the main component in natural gas, by causing a chemical reaction between hydrogen and CO2 in a reactor vessel filled with a catalyst.
It uses emitted CO2 separated and captured from industrial facilities. As the CO2 generated when combusting synthesized methane is considered to be offset by the separated and captured CO2, it is expected that CO2 emissions can be significantly reduced by using hydrogen generated by electrolyzing water with electricity derived from renewable energy, the Working Group said.
A technical paper describing the details of the calculation procedures and evaluation involved in this study was published in the journal of Institute of Japan Marine Engineering, Vol. 56, No. 4.
"In order to verify the feasibility of carbon recycled methane as a ship fuel, the WG will continue to work on issues such as CO2 transportation by large-scale liquified CO2 carrier vessels, supply of hydrogen from renewable energy, prevention of methane slip, supply infrastructure of liquefied methanation fuel, and economic viability," the working group said.
Methane slip is the unburned and exhausted methane from the main engine. Methane is GHG with 25 times the greenhouse effect of CO2.
To explore the feasibility of the concept of utilizing methanation technology for zero-emission ship fuels, the WG was formed within Japan’s CCR Study Group, and started its activity in July 2020.
The working group said it has assumed and evaluated the following four processes as the supply chain for carbon-recycled methane fuel: (1) CO2 separation and capture, (2) CO2 transportation, (3) methanation fuel synthesis, and (4) methanation fuel liquefaction.
"As a result, the CO2 emission per unit calorific value of carbon-recycled methane fuel by methanation was calculated as approximately 27-gCO2/MJ (regarded as Well to Propeller)," the group said.
"This figure is comparable to other alternative fuel candidates generally recognized as zero-emission fuels, confirming that carbon-recycled methane can be recognized as zero-emission ship fuel. In addition, further reduction to approximately 20-gCO2/MJ is expected by improving the efficiency of the separation and capture technology, and using electricity produced from renewable energy," it added.