Cognitive Technology to Reduce Motion Sickness in Amphibious Vehicles
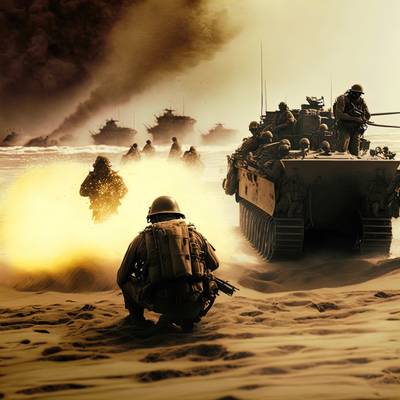
Hyundai Mobis has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Republic of Korea Marine Corps for cooperation on technology that is expected to alleviate motion sickness for marines traversing rough terrains from sea to land, enhancing combat performance.
Last year, Hyundai Mobis developed the 'Smart Cabin Controller,' analyzing a driver's posture, heart rate, and brainwaves to prevent drowsiness, stress, and motion sickness.
The MoU marks the first application of the technology in the broader mobility sector, and the company anticipates its expansion into defense, maritime, and aviation transportation.
Motion sickness generally occurs when there is a discrepancy between what the eyes see and what the body feels regarding movement direction – for example, looking sideways in a moving vehicle while the body senses forward motion. This is also why seats facing the opposite direction on a train are less preferred.
Hyundai Mobis' motion sickness reduction technology integrates autonomous driving with passenger cognitive technologies that involve real-time monitoring of posture, heart rate, and brainwaves using sensors. Based on this biometric data, simulating the senses of sight, hearing, smell, and touch can minimize motion sickness. The company says its technology can prevent motion sickness by up to 70% and reduce the symptoms by 40%.
Hyundai Mobis plans to operate this technology in amphibious assault vehicles and, in collaboration with the Marine Corps, gather key data by the first half of next year. The company aims to deploy it in combat training and systematically analyze motion sickness-inducing factors to enhance the technology's efficacy.