Satellites Reveal Worldwide Ship Traffic Up 300%
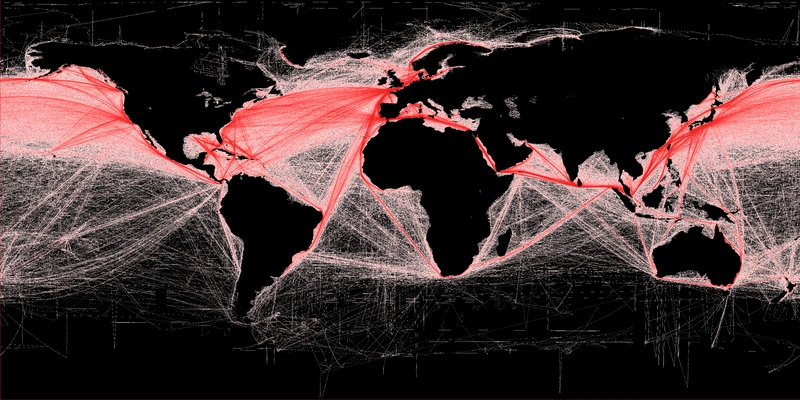
Maritime traffic on the world’s oceans has increased four-fold over the past 20 years, according to a new study quantifying global ship traffic. The research used satellite data to estimate the number of vessels on the ocean every year between 1992 and 2012. The number of ships traversing the oceans grew by 60% between 1992 and 2002. Shipping traffic grew even faster during the second decade of the study, peaking at a rate of increase of 10 percent per year in 2011. Traffic increased in every ocean during the 20 years of the study, except off the coast of Somalia, where increasing piracy has almost completely halted commercial shipping since 2006. In the Indian Ocean, where the world’s busiest shipping lanes are located, ship traffic grew by more than 300 percent over the 20-year period, according to the research. International trade and the sizes of merchant fleets have both enlarged rapidly over the past two decades, explaining the steep rise in ship traffic, the study reports. The new analysis has been accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American Geophysical Union. Jean Tournadre is a geophysicist at Ifremer, the French Institute for the Exploitation of the Sea in Plouzane, and the study author.
The new dataset will provide scientists with invaluable insights into the patterns of ship traffic and the traffic’s effect on the environment, said Batuhan Osmanoglu, a radar systems engineer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Green Belt, Md., who was not involved in the study. “The nice thing about this study is that they have a unique dataset, that maybe we’re looking at for the first time,” he said. “Whenever you have a unique dataset you can quite easily learn something new.”
The new method outlined in the study uses altimeters, instruments that measure altitude, aboard satellites to detect the location of ships at sea, similar to the way these instruments have been used to track icebergs. The altimeter sends a radar pulse down to Earth from the satellite and constructs an image of the surface based on the time it takes the pulse to bounce back to the instrument and the shape of the pulse when it arrives. The method works similar to throwing a ping pong ball at the ground: if you know the velocity of the ball and the time it takes to bounce back to your hand, then you can calculate how far from the ground you are. The shape of the returning pulse can tell you something about the features on the ground. A smooth target like the ocean will bounce back an expected pulse shape, but if something like an iceberg, island or ship is present, the shape of the echo will change.
In 2007, Tournadre was poring over hordes of satellite data for signs of icebergs in polar seas, when he noticed an odd shape in the data. “We had some unconventional data in a region, and careful analysis showed us that it was a lighthouse near shipping lanes,” he said. “As we processed the data over the whole globe, we also detected ships.”
Tournadre found that the altimetry data accurately reproduced known shipping lanes and could be used to estimate the number of vessels on the ocean worldwide. The study used altimetry data from seven different satellites to map ship traffic from 1992 to 2012. However, Tournadre also cautions that some of the growth he has seen in ship traffic could be overestimated because ships, especially container ships, have become larger over the past two decades and possibly easier to detect with altimetry data.
(As published in the December 2014 edition of Maritime Reporter & Engineering News - http://magazines.marinelink.com/Magazines/MaritimeReporter)
Related News


